Exposing the Dark Secrets of Deepfake Technology: Unmasking Scammer Tactics
INTRODUCTION
In an era of rapid technological advancement, deepfake technology has emerged as a powerful tool for creating hyper-realistic, manipulated videos and audio recordings. While deepfakes have legitimate applications in entertainment and art, they are increasingly being exploited by scammers and malicious actors for fraudulent purposes. This article aims to shed light on the inner workings of deepfake technology and unravel the tactics employed by scammers to deceive and defraud individuals and organizations.
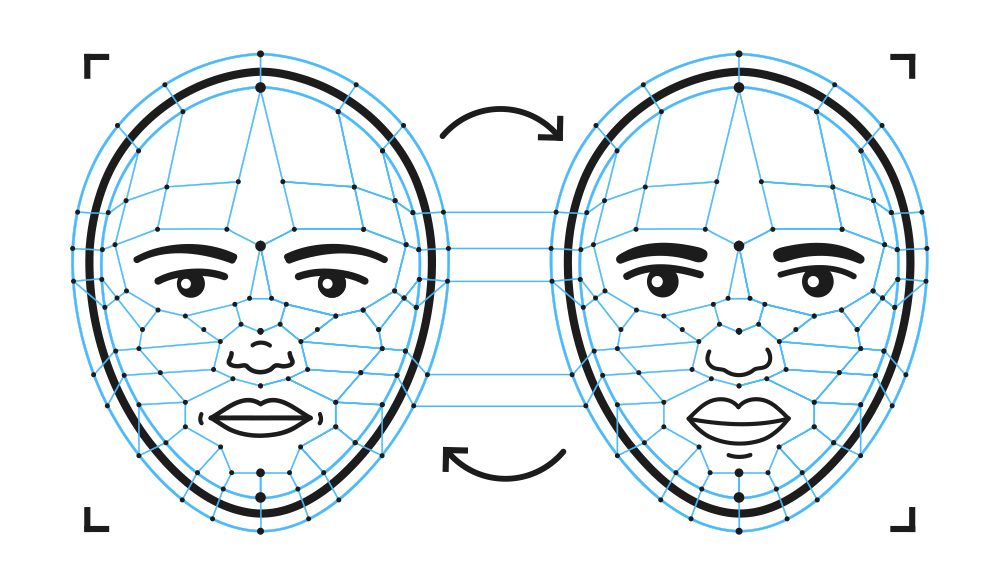
Deepfake technology is a sophisticated form of artificial intelligence (AI) that is used to create highly realistic but entirely fabricated videos or audio recordings. The term “deepfake” is a portmanteau of “deep learning” and “fake.”
Understanding Deepfake Technology
Deep Learning Algorithms: Deepfakes are created using advanced deep learning algorithms, particularly Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), which can generate highly convincing fake media.
Data Collection: Scammers often gather extensive data on their targets, including images, voice recordings, and personal information, to craft more convincing deepfakes.
Realistic Facial Mapping: Deepfake creators use AI to map a target’s face onto a source video, allowing them to manipulate facial expressions and movements with precision.
Voice Cloning: Scammers employ voice cloning technology to mimic a person’s voice, making it appear as if the target is speaking in the manipulated video or audio.
Scammer Tactics
Impersonation: Scammers use deepfake technology to impersonate trusted individuals, such as company executives or family members, to deceive their targets.
Business Fraud: Fraudsters create fake videos to manipulate stock prices or manipulate financial data, causing harm to investors and companies.
Identity Theft: Deepfake voices and videos are employed to steal identities, enabling scammers to access personal accounts and sensitive information.
Fake Interviews: Scammers create deepfake interviews with prominent figures to spread false information or manipulate public perception.
Extortion: Perpetrators use fabricated deepfake videos to extort money or favors from their victims, threatening to release damaging content.
Detecting Deepfakes
Pay attention to visual cues: Deepfake videos may have subtle visual cues that can reveal that they have been manipulated. For example, there may be inconsistencies in lighting, shadows, or reflections. Additionally, the subject of the video may not blink as often as a real person would, or their facial expressions may appear unnatural.
Listen for audio cues: Deepfake videos may also have audio cues that can give away their artificial nature. For example, the audio may not sync up perfectly with the video, or there may be anomalies in the background noise.
Advanced AI Tools (Software): Organizations and individuals can employ AI-based deepfake detection tools that analyze videos and audio for anomalies and inconsistencies.
Verification Protocols: Implementing multi-step verification processes can help ensure the authenticity of video and audio communications.
Source Verification: Verify the source of any unusual or sensitive content to reduce the risk of falling victim to deepfake scams.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Legislation: Governments worldwide are enacting laws to combat deepfake technology misuse, imposing severe penalties on offenders.
Ethical Considerations: Deepfake technology raises ethical questions about privacy, consent, and responsible use, necessitating public discourse and awareness.
Conclusion
Deepfake technology, with its potential for deception and harm, poses a significant threat in today’s digital landscape. By understanding the inner workings of deepfake technology and being aware of the tactics employed by scammers, individuals and organizations can take proactive steps to protect themselves from falling victim to deepfake scams. Additionally, promoting ethical and responsible use of this technology is crucial to mitigating its negative impacts on society.












2 comments